PT-141 (BREMELANOTIDE)
Peptide Data Sheet for Pharmacists and Compounding Professionals
BASIC INFORMATION
Name: PT-141 (Bremelanotide)
Class: Melanocortin receptor agonist
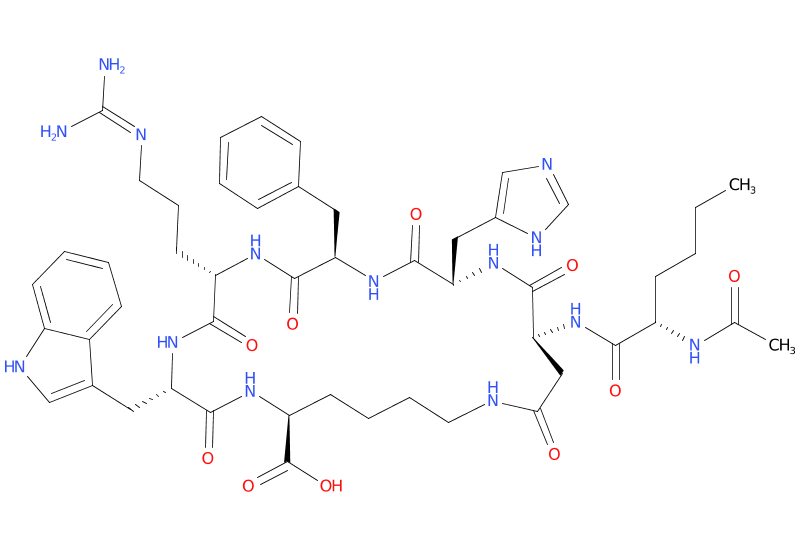
Structure: Cyclic heptapeptide analog of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)
Molecular Weight: 1025.2 g/mol
Sequence: Ac-Nle-cyclo[Asp-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys]-OH
Brand Name: Vyleesi®
Available Forms:
- FDA-approved injectable solution (Vyleesi®)
- Compounded formulations (subject to regulatory requirements)
- Research peptide
REGULATORY STATUS
FDA Status
- Vyleesi®: Approved in June 2019 for the treatment of acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women.
- Not approved for men or postmenopausal women.
- Available only by prescription.
Legal Considerations
- Prescription-only medication.
- Not approved for use to improve sexual performance outside of its approved indication.
- Compounding pharmacies may prepare custom formulations under appropriate prescribing and in compliance with regulations.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
PT-141 (Bremelanotide) is a synthetic analog of α-MSH that:
- Acts as a non-selective agonist of melanocortin receptors (primarily MC3R and MC4R) in the central nervous system.
- Activation of these receptors is thought to modulate pathways involved in sexual desire and arousal.
- Unlike PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil), PT-141 does not directly affect peripheral blood flow to the genitals.
- Its effects are centrally mediated, influencing sexual desire and function through neural pathways.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Parameter | Value | Notes | |———–|——-|——-| | Absorption | Rapid after subcutaneous administration | Peak plasma concentration: ~1 hour | | Distribution | Volume of distribution: ~2.7 L | Plasma protein binding: ~21% | | Metabolism | Extensively metabolized by hydrolysis | Specific pathways not fully elucidated | | Elimination | Half-life: ~2.7 hours (range 1.9-4.0 hours) | Primarily excreted in urine (64.8%) and feces (22.8%) |
CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
FDA-Approved Indications
- Treatment of acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women.
- Should only be used in women who have low sexual desire that is troubling to them and is not caused by:
- Co-existing medical or psychiatric conditions
- Problems within the relationship
- Effects of medications or other drug substances
Off-Label/Investigational Uses
- Male erectile dysfunction (some studies have shown efficacy)
- Sexual arousal disorder in women (broader than HSDD)
DOSING GUIDELINES
FDA-Approved Dosing (Vyleesi®)
| Indication | Dose | Administration | |————|——|—————-| | HSDD in premenopausal women | 1.75 mg | Subcutaneously, as needed, at least 45 minutes before anticipated sexual activity |
Important Dosing Considerations:
- Maximum one dose within a 24-hour period.
- Maximum 8 doses per month.
- If no improvement in HSDD after 8 weeks, discontinue treatment.
ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous Injection
- Administer in the abdomen or thigh.
- Rotate injection sites.
- Supplied as a single-dose prefilled autoinjector.
- Store at room temperature (20°C to 25°C; 68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
- Do not freeze.
SAFETY PROFILE
Contraindications
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Known cardiovascular disease
- Hypersensitivity to bremelanotide or any excipients
Warnings and Precautions
- Transient Increase in Blood Pressure and Decrease in Heart Rate: Occurs after each dose, usually resolves within 12 hours. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate in patients at risk.
- Nausea: Common, especially with the first dose. May require antiemetic medication.
- Focal Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin (face, gums, breasts) may occur, particularly in patients with darker skin. More common with daily use (not the approved dosing regimen).
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions with Naltrexone: Concomitant use with naltrexone (oral) may lead to a failure of naltrexone treatment.
Common Adverse Effects
| System | Adverse Effects | Approximate Incidence | |——–|—————-|————————| | Gastrointestinal | Nausea | ~40% | | | Vomiting | ~13% | | Nervous System | Headache | ~11% | | | Flushing | ~20% | | | Dizziness | ~5% | | General | Injection site reactions | ~13% | | | Fatigue | ~4% |
Drug Interactions
- Naltrexone: May interfere with the efficacy of naltrexone. Avoid concomitant use.
- Indomethacin: May increase bremelanotide exposure. Use with caution.
- Rosuvastatin: May increase bremelanotide exposure. Use with caution.
- Drugs that affect GI motility: May alter absorption of bremelanotide, but clinical significance is unknown.
SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Renal Impairment
- Mild to moderate: No dose adjustment needed.
- Severe (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m²): Use with caution, may increase exposure.
- End-stage renal disease: Not recommended.
Hepatic Impairment
- Mild to moderate: No dose adjustment needed.
- Severe: Not studied, use with caution.
Geriatric Patients
- Not indicated for postmenopausal women.
- Safety and efficacy not established in geriatric populations.
Pregnancy and Lactation
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. Advise premenopausal women to use effective contraception during treatment. Discontinue if pregnancy occurs.
- Lactation: Unknown if excreted in human milk. Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment.
PHARMACIST GUIDANCE
Compounding Considerations
- Vyleesi® is available as an FDA-approved product.
- Compounding may be considered if specific patient needs cannot be met by the commercial product (e.g., different dosage form, allergen removal), but must comply with all relevant regulations (USP <795>, <797>, state laws).
- Stability and compatibility data for compounded formulations may be limited.
- Requires aseptic technique for sterile preparations.
Storage and Handling
- Vyleesi® Autoinjector: Store at room temperature (20°C to 25°C; 68°F to 77°F).
- Compounded Preparations: Follow specific stability data and USP guidelines. Typically refrigerated for lyophilized powder and reconstituted solutions.
Patient Counseling Points
- Administration Technique
- Proper subcutaneous injection technique for autoinjector.
- Importance of injection site rotation (abdomen or thigh).
- Administer at least 45 minutes before sexual activity.
- Dosing Limitations
- No more than one dose in 24 hours.
- No more than 8 doses per month.
- Common Side Effects
- Nausea is common, especially with the first dose; may take antiemetic if prescribed.
- Flushing, headache, and injection site reactions may occur.
- Report persistent or severe side effects.
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
- May cause a temporary increase in blood pressure and decrease in heart rate.
- Patients with cardiovascular risk factors should be monitored.
- Skin Hyperpigmentation
- Potential for darkening of skin, especially with more frequent use than approved.
- Report any unusual skin changes.
- Pregnancy and Contraception
- Advise use of effective contraception.
- Discontinue if pregnancy is suspected or confirmed.
- When to Discontinue
- If HSDD does not improve after 8 weeks.
MAXIMIZING THERAPEUTIC OUTCOMES
Optimizing Efficacy
- Ensure proper diagnosis of acquired, generalized HSDD.
- Rule out other causes of low sexual desire.
- Counsel on realistic expectations and proper use.
- Administer as needed, at least 45 minutes before sexual activity.
Managing Common Challenges
- Nausea: Consider prophylactic antiemetic if severe or persistent.
- Injection Site Reactions: Proper technique, site rotation.
- Cost and Access: Discuss insurance coverage and patient assistance programs if available.
REFERENCES
- FDA. Vyleesi (bremelanotide) Prescribing Information. June 2019.
- Kingsberg SA, et al. Bremelanotide for the Treatment of Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder: Two Randomized Phase 3 Trials. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134(5):899-908.
- Simon JA, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Bremelanotide for Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder in Premenopausal Women: Results from Two Phase 3 Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials. J Sex Med. 2019;16(11):1784-1796.
- Molinoff PB, et al. Bremelanotide: a novel melanocortin agonist for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women. Womens Health (Lond). 2010;6(5):641-50.
