TIRZEPATIDE
Peptide Data Sheet for Pharmacists and Compounding Professionals
BASIC INFORMATION
Name: Tirzepatide
Class: Dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist
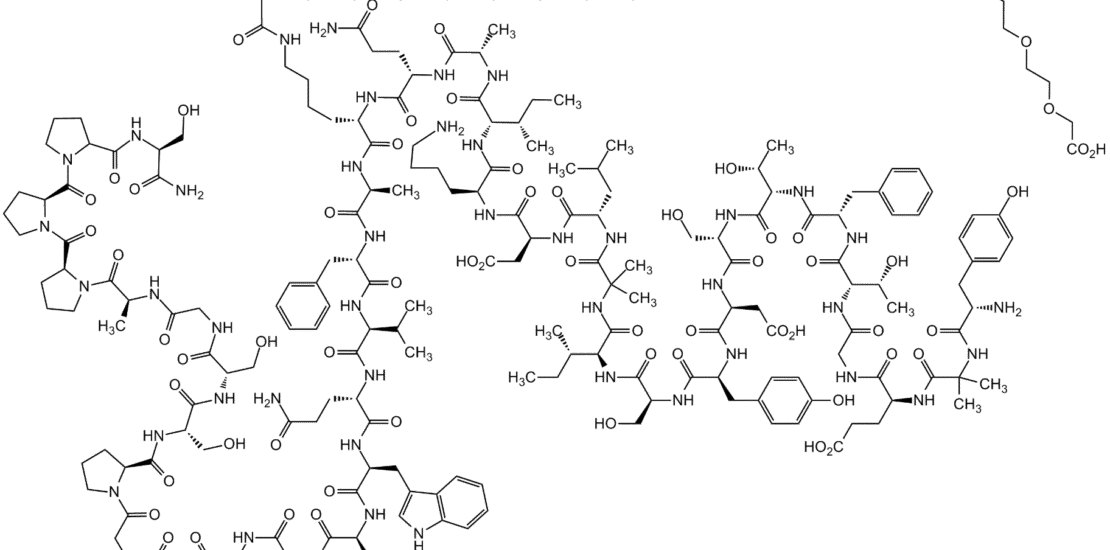
Structure: 39-amino acid synthetic peptide
Molecular Weight: 4813.58 g/mol
Chemical Modifications:
- C20 fatty diacid moiety attached to lysine at position 20
- Amino acid substitutions to enhance stability and receptor binding
Available Forms:
- FDA-approved injectable solution (Mounjaro®, Zepbound®)
- Compounded formulations (subject to regulatory requirements)
REGULATORY STATUS
FDA Status
- Mounjaro®: Approved for type 2 diabetes management (May 2022)
- Zepbound®: Approved for chronic weight management (November 2023)
Compounding Considerations
- Compounding must comply with USP <797> standards
- Not eligible for compounding when FDA-approved versions are commercially available unless clinical need for modification is documented
- Requires sterile compounding techniques
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Tirzepatide has a unique dual mechanism:
- GIP Receptor Activation:
- Enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion
- Decreases glucagon secretion
- Improves insulin sensitivity
- GLP-1 Receptor Activation:
- Increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion
- Decreases inappropriate glucagon secretion
- Slows gastric emptying
- Increases satiety and reduces food intake
The dual receptor activation provides enhanced glycemic control and weight loss compared to selective GLP-1 receptor agonists.
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Parameter | Value | Notes | |———–|——-|——-| | Absorption | Subcutaneous: ~80% bioavailability | Peak plasma concentration: 8-72 hours | | Distribution | Volume of distribution: ~10.3 L | >99% plasma protein bound | | Metabolism | Proteolytic cleavage of peptide backbone | Resistant to DPP-4 degradation | | Elimination | Half-life: ~5 days (120 hours) | Primarily renal clearance |
CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
FDA-Approved Indications
- Type 2 Diabetes Management (Mounjaro®)
- Improves glycemic control as adjunct to diet and exercise
- Typical HbA1c reduction: 1.8-2.1% (10 mg dose)
- Comparative efficacy: Superior to semaglutide 1 mg in head-to-head trials
- Chronic Weight Management (Zepbound®)
- For adults with BMI ≥30 kg/m², or ≥27 kg/m² with weight-related comorbidity
- Average weight loss: 15-20.9% of body weight over 72 weeks
- Maintenance of weight loss with continued therapy
Off-Label/Investigational Uses
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Cardiovascular risk reduction
- Obesity-related complications
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
DOSING GUIDELINES
Type 2 Diabetes (Mounjaro®)
| Week | Dose | Administration | |——|——|—————-| | 1-4 | 2.5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 5-8 | 5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 9-12 | 7.5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 13-16 | 10 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 17+ (if needed) | 12.5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | Maintenance (if needed) | 15 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous |
Weight Management (Zepbound®)
| Week | Dose | Administration | |——|——|—————-| | 1-4 | 2.5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 5-8 | 5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 9-12 | 7.5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 13-16 | 10 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | 17+ (if needed) | 12.5 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous | | Maintenance (if needed) | 15 mg | Once weekly, subcutaneous |
Dose Adjustments:
- Dose escalation may be delayed based on tolerability
- Temporary dose reduction may be considered for tolerability issues
- Patients with renal impairment may require slower titration
ADMINISTRATION
Subcutaneous Injection
- Administer in abdomen, thigh, or upper arm
- Rotate injection sites
- May be administered without regard to meals
- Store refrigerated (2-8°C/36-46°F)
- May be stored at room temperature (up to 30°C/86°F) for up to 21 days
SAFETY PROFILE
Contraindications
- Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2)
- Hypersensitivity to tirzepatide or any excipients
- Pregnancy (Zepbound®)
Warnings and Precautions
- Boxed Warning: Risk of thyroid C-cell tumors
- Pancreatitis
- Diabetic retinopathy complications
- Acute kidney injury
- Hypoglycemia (when used with insulin or insulin secretagogues)
- Acute gallbladder disease
- Hypersensitivity reactions
Common Adverse Effects
| System | Adverse Effects | Approximate Incidence | |——–|—————-|————————| | Gastrointestinal | Nausea | 17-25% | | | Vomiting | 6-12% | | | Diarrhea | 13-17% | | | Abdominal pain | 6-10% | | | Constipation | 5-7% | | General | Fatigue | 5-7% | | | Injection site reactions | 1-3% | | Metabolic | Decreased appetite | 10-12% |
Drug Interactions
- Delayed absorption of oral medications due to slowed gastric emptying
- Increased risk of hypoglycemia when used with insulin or insulin secretagogues
- Potential additive effects with other medications that cause hypoglycemia
SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Renal Impairment
- No dose adjustment required for mild to moderate renal impairment
- Limited experience in severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m²)
- Use caution and monitor renal function when initiating or escalating doses
Hepatic Impairment
- No dose adjustment required for mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment
- Limited clinical experience in severe hepatic impairment
Geriatric Patients
- No dose adjustment required based on age
- Greater sensitivity in some older individuals
- Start at lower doses and titrate more slowly if needed
Pregnancy and Lactation
- Pregnancy: Not recommended for use in pregnancy
- Lactation: Unknown if excreted in human milk; use caution
PHARMACIST GUIDANCE
Compounding Considerations
- Requires aseptic technique and sterile compounding environment
- Stability affected by temperature, pH, and mechanical agitation
- Incompatible with strongly acidic or basic solutions
- Adhere to USP <797> standards for sterile compounding
Storage and Handling
- Store in refrigerator (2-8°C/36-46°F)
- Protect from light
- Do not freeze
- Discard if frozen
- Stable at room temperature for up to 21 days
Patient Counseling Points
- Administration Technique
- Proper subcutaneous injection technique
- Importance of injection site rotation
- Proper disposal of needles and syringes
- Gastrointestinal Side Effects
- Typically transient and decrease over time
- Small, frequent meals may help
- Adequate hydration important
- Contact healthcare provider if severe or persistent
- Hypoglycemia Risk
- Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia
- Proper management of hypoglycemia
- Importance of blood glucose monitoring
- Monitoring Parameters
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose
- Regular monitoring of weight
- Regular monitoring of renal function
- Regular monitoring of pancreatic enzymes if symptoms of pancreatitis
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Severe abdominal pain (potential pancreatitis)
- Persistent vomiting or inability to maintain hydration
- Signs of allergic reaction
- Visual changes
MAXIMIZING THERAPEUTIC OUTCOMES
Optimizing Efficacy
- Gradual dose titration minimizes GI side effects and improves tolerability
- Combination with lifestyle modifications enhances weight loss and glycemic control
- Patient education improves adherence and outcomes
- Regular follow-up and monitoring optimizes dose and manages side effects
Managing Common Challenges
- GI Side Effects: Slow titration, small frequent meals, adequate hydration
- Injection Site Reactions: Proper technique, site rotation, room temperature injection
- Adherence: Weekly dosing improves compliance compared to daily medications
- Cost: Patient assistance programs, insurance prior authorizations
Comparative Efficacy
| Outcome | Tirzepatide | Semaglutide | Notes | |———|————-|————-|——-| | HbA1c Reduction | 1.8-2.1% | 1.0-1.8% | Head-to-head SURPASS-2 trial | | Weight Loss | 15-20.9% | 15-18% | Higher average weight loss with tirzepatide | | GI Side Effects | Similar profile | Similar profile | Comparable tolerability |
REFERENCES
- FDA. Mounjaro (tirzepatide) Prescribing Information.
- FDA. Zepbound (tirzepatide) Prescribing Information.
- Frías JP, et al. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(6):503-515.
- Jastreboff AM, et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(3):205-216.
- Min T, Bain SC. The Role of Tirzepatide, Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS Clinical Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2021;12(1):143-157.
