SERMORELIN
Peptide Data Sheet for Pharmacists and Compounding Professionals
BASIC INFORMATION
Name: Sermorelin (GRF 1-29)
Class: Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) analog
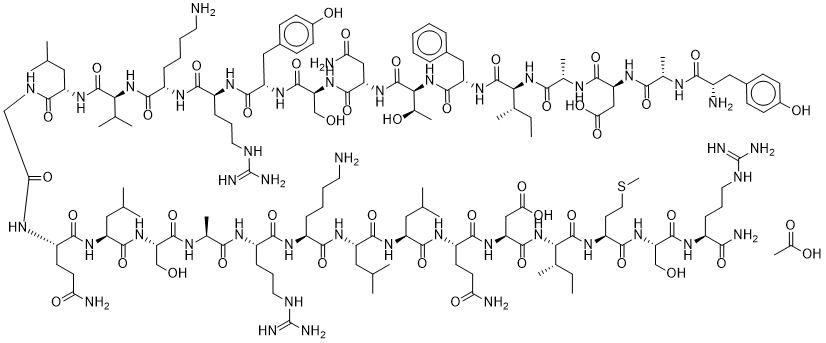
Structure: 29-amino acid peptide, N-terminal fragment of GHRH
Molecular Weight: 3357.9 g/mol
Sequence: Tyr-Ala-Asp-Ala-Ile-Phe-Thr-Asn-Ser-Tyr-Arg-Lys-Val-Leu-Gly-Gln-Leu-Ser-Ala-Arg-Lys-Leu-Leu-Gln-Asp-Ile-Met-Ser-Arg-NH₂
Chemical Modifications:
- C-terminal amidation
- Represents the first 29 amino acids of the 44-amino acid human GHRH
Available Forms:
- Previously FDA-approved as Geref® (discontinued in 2008)
- Compounded formulations (subject to regulatory requirements)
- Research peptide
REGULATORY STATUS
FDA Status
- Previously FDA-approved for diagnostic evaluation of growth hormone deficiency in children
- Geref® (sermorelin acetate) was discontinued in 2008 (not for safety reasons)
- Currently not available as an FDA-approved medication
- May be legally compounded by pharmacies under certain circumstances
Legal Considerations
- Unlike some peptides, sermorelin has historical FDA approval
- Compounding pharmacies may prepare sermorelin under appropriate prescribing
- Must be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider for a legitimate medical purpose
- Subject to state pharmacy regulations and USP standards
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Sermorelin is a synthetic analog of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) that:
- Binds to GHRH receptors in the anterior pituitary gland
- Stimulates the synthesis and pulsatile release of endogenous growth hormone (GH)
- Increases insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) production as a secondary effect
- Preserves physiological pulsatile pattern of GH release (unlike exogenous GH)
- May help maintain pituitary function
Unlike exogenous growth hormone administration, sermorelin:
- Maintains negative feedback regulation of the GH axis
- Allows for natural fluctuations in GH levels
- May have a more physiological effect profile
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Parameter | Value | Notes | |———–|——-|——-| | Absorption | Rapid after subcutaneous injection | Bioavailability: ~0.5-1.5% | | Distribution | Limited data available | Primarily acts on pituitary receptors | | Metabolism | Rapid enzymatic degradation | Primarily by dipeptidyl peptidase IV | | Elimination | Half-life: ~10-20 minutes | Rapid clearance limits duration of action |
CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Historical FDA-Approved Indications
- Diagnostic evaluation of growth hormone secretion in children
Potential Applications (Off-Label/Investigational)
Note: Evidence quality varies; clinical judgment required.
- Age-related growth hormone decline
- Body composition improvement
- Sleep quality enhancement
- Recovery from injury
- Cognitive function (limited evidence)
DOSING GUIDELINES
Historical FDA-Approved Dosing
- Diagnostic testing: 1 mcg/kg body weight, administered IV or SC
Common Off-Label Dosing Practices
Note: Not FDA-approved dosing regimens; clinical judgment required.
| Purpose | Typical Dose Range | Frequency | |———|——————-|———–| | GH stimulation | 100-500 mcg | Once daily, typically before bedtime | | Anti-aging protocols | 200-300 mcg | Once daily, typically before bedtime |
Administration Timing:
- Typically administered in the evening to align with natural GH pulses
- Consistent timing recommended for optimal effect
ADMINISTRATION
Routes
- Subcutaneous injection (most common)
- Intravenous injection (less common, primarily for diagnostic use)
Preparation and Administration
- Reconstitute with bacteriostatic water or sterile saline
- Store reconstituted solution refrigerated (2-8°C/36-46°F)
- Administer using insulin syringe or similar
- Rotate injection sites
- Typical injection sites: abdomen, thigh, or deltoid
SAFETY PROFILE
Adverse Effects
| Frequency | Adverse Effects | |———–|—————-| | Common | Injection site reactions (redness, pain, swelling)<br>Flushing<br>Headache<br>Dizziness | | Less Common | Nausea<br>Altered taste sensation<br>Hyperactivity<br>Dysphagia | | Rare | Hypersensitivity reactions<br>Antibody formation<br>Chest tightness |
Potential Risks and Concerns
- Potential for growth promotion in pre-existing cancers (theoretical)
- Glucose metabolism alterations
- Fluid retention
- Joint pain
- Unknown long-term effects with extended use
Contraindications
- Active malignancy
- Intracranial lesions
- Pregnancy and lactation
- Hypersensitivity to sermorelin or mannitol
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Pregnancy and Lactation
- No adequate studies in pregnant women
- Not recommended during pregnancy or lactation
Pediatric
- Historically used diagnostically in children
- Not recommended for off-label use in pediatric populations
- May affect growth plates and development
Geriatric
- No specific dose adjustments required
- May have increased sensitivity to adverse effects
- Monitor for fluid retention and arthralgia
DRUG INTERACTIONS
| Interacting Drug | Effect | Management | |——————|——–|————| | Glucocorticoids | May inhibit response to sermorelin | Monitor efficacy | | Opioid analgesics | May blunt GH response | Consider timing separation | | Somatostatin analogs | Antagonize sermorelin effects | Avoid combination | | Aromatase inhibitors | May enhance GH response | Monitor for enhanced effects | | Insulin/oral hypoglycemics | Potential for altered glucose metabolism | Monitor blood glucose |
PHARMACIST GUIDANCE
Compounding Considerations
- Requires aseptic technique and sterile compounding environment
- Stability affected by temperature and mechanical agitation
- Typical beyond-use date: 30 days refrigerated after reconstitution
- Adhere to USP <797> standards for sterile compounding
- Consider preservative-free formulations for patients with sensitivities
Storage and Handling
- Store lyophilized peptide at -20°C
- Reconstituted solutions stored at 2-8°C
- Protect from light
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
- Discard if solution appears cloudy or contains particles
Patient Counseling Points
- Administration Technique
- Proper subcutaneous injection technique
- Importance of injection site rotation
- Proper disposal of needles and syringes
- Storage Requirements
- Keep refrigerated
- Do not freeze reconstituted solution
- Discard after beyond-use date
- Common Side Effects
- Injection site reactions typically mild and transient
- Headache and flushing usually resolve with continued use
- When to contact healthcare provider
- Monitoring Parameters
- Signs of fluid retention
- Changes in blood glucose (diabetic patients)
- Follow-up laboratory testing as directed
- Lifestyle Considerations
- Optimal timing (evening administration)
- Potential benefits of adequate sleep
- Importance of consistent administration schedule
MONITORING RECOMMENDATIONS
Laboratory Parameters
- IGF-1 levels (baseline and periodic)
- Growth hormone stimulation (if clinically indicated)
- Fasting blood glucose
- Hemoglobin A1c (in diabetic patients)
- Thyroid function tests
Clinical Monitoring
- Body composition changes
- Sleep quality
- Energy levels
- Adverse effects
- Quality of life measures
REFERENCES
- Prakash A, Goa KL. Sermorelin: a review of its use in the diagnosis and treatment of children with idiopathic growth hormone deficiency. BioDrugs. 1999;12(2):139-57.
- Walker RF. Sermorelin: a better approach to management of adult-onset growth hormone insufficiency? Clin Interv Aging. 2006;1(4):307-308.
- Merriam GR, et al. Growth hormone releasing hormone and growth hormone secretagogues in normal aging. Endocrine. 2003;22(1):41-8.
- FDA. Geref (sermorelin acetate) Prescribing Information (historical).
- Vittone J, et al. Effects of single nightly injections of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH 1-29) in healthy elderly men. Metabolism. 1997;46(1):89-96.
