MOTS-C
Peptide Data Sheet for Pharmacists and Compounding Professionals
BASIC INFORMATION
Name: MOTS-c (Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the Twelve S rRNA type-c)
Class: Mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP)
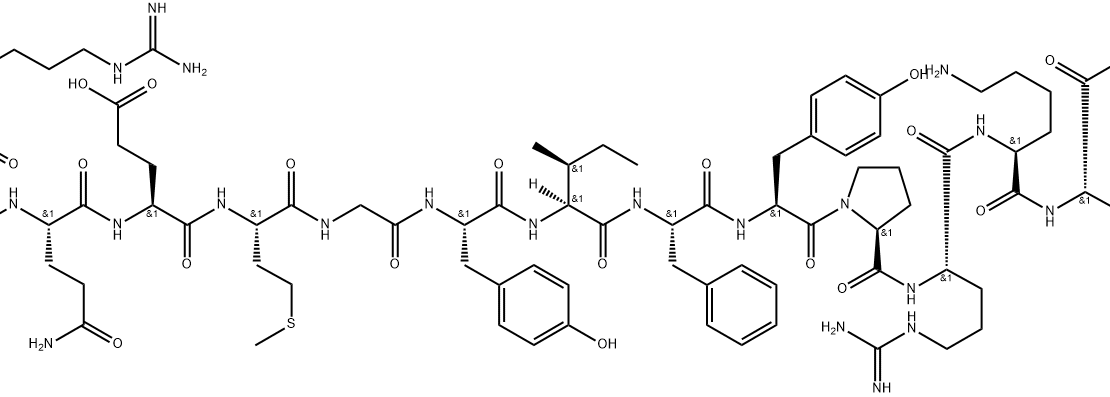
Structure: 16-amino acid peptide
Molecular Weight: 1618.8 g/mol
Sequence: Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg
Origin: Encoded by the mitochondrial genome in the 12S rRNA region
Available Forms:
- Research peptide
- Not available as an FDA-approved medication
- Compounded formulations (subject to regulatory restrictions)
REGULATORY STATUS
FDA Status
- Not FDA-approved for any medical condition
- Classified as a research compound
- FDA has clarified it is among peptides unlawful to use in making compounded medications
- Not a legitimate dietary ingredient and cannot legally be used in dietary supplements
Sports/Anti-Doping Status
- Prohibited at all times under Section 4.4 Metabolic Modulators, 4.4.1. Activators of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) on the World Anti-Doping Agency Prohibited List
- Athletes cannot get a Therapeutic Use Exemption (TUE) for MOTS-c because there is no approved therapeutic use
MECHANISM OF ACTION
MOTS-c is a mitochondrial-derived peptide that:
- Activates the 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway
- Regulates metabolic homeostasis
- Promotes glucose utilization in skeletal muscle
- Enhances cellular glucose uptake
- Increases insulin sensitivity
- Regulates skeletal muscle metabolism and gene expression
- Inhibits oxidative stress
- Can activate NF-κB to inhibit inflammation
- Transfers to the nucleus during metabolic stress to direct nuclear gene expression
The activation of AMPK leads to:
- Increased glucose uptake via GLUT4 translocation
- Enhanced fatty acid oxidation
- Mitochondrial biogenesis
- Reduced oxidative stress
PHARMACOKINETICS
| Parameter | Value | Notes | |———–|——-|——-| | Expression | Co-expressed with mitochondria in different tissues | Present in multiple tissue types | | Circulation | Present in plasma | Levels decrease with age | | Response to Exercise | Increases ~11.9-fold in skeletal muscle following exercise | Circulating levels increase 1.6-fold during exercise | | Duration | Levels increase 1.5-fold after exercise | Return to baseline after ~4 hours |
Note: Pharmacokinetic data is primarily derived from limited human studies and animal research.
POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS (INVESTIGATIONAL)
Note: All applications are investigational and not FDA-approved. This information is provided for educational purposes only.
Metabolic
- Insulin resistance
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
Age-Related
- Age-related metabolic decline
- Sarcopenia
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
Other Investigational Areas
- Exercise performance enhancement
- Cardiovascular protection
- Neuroprotection
- Inflammation reduction
ADMINISTRATION (INVESTIGATIONAL)
Routes
- Subcutaneous injection (most common in research)
- Intravenous injection (less common, research only)
Investigational Dosing
Note: No established safe or effective dosing regimen exists. The following information is based on research protocols and is not a recommendation for clinical use.
| Setting | Investigational Dose Range | Frequency | |———|—————————-|———–| | Research protocols | 5-10 mg | Daily |
SAFETY PROFILE
Reported Adverse Effects
Note: Safety data is extremely limited and primarily from anecdotal reports and animal studies.
- Increased heart rate or heart palpitations
- Injection site irritation
- Insomnia
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea
Potential Risks and Concerns
- Unknown long-term effects
- Potential metabolic disturbances
- Potential for growth promotion in pre-existing cancers (theoretical)
- Lack of quality control in commercially available products
- Potential for contamination in non-pharmaceutical grade products
- Unknown drug interactions
Contraindications (Theoretical)
- Active malignancy
- Pregnancy and lactation
- Children and adolescents
- Uncontrolled cardiovascular disease
- Uncontrolled diabetes
SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Pregnancy and Lactation
- No human data available
- Avoid use due to unknown risks
Pediatric
- No human data available
- Not recommended for use in pediatric populations
Geriatric
- No specific data available
- Potentially higher risk of adverse effects
PHARMACIST GUIDANCE
Compounding Considerations
- FDA has clarified that MOTS-c is among peptides unlawful to use in making compounded medications
- Pharmacists should be aware of regulatory restrictions
- If compounding is legally permitted in specific circumstances:
- Requires aseptic technique and sterile compounding environment
- Stability affected by temperature and mechanical agitation
- Adhere to USP <797> standards for sterile compounding
Storage and Handling (Research Settings)
- Store lyophilized peptide at -20°C
- Reconstituted solutions typically stored at 2-8°C
- Use within 14 days of reconstitution
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
- Protect from light
Patient Counseling Points
- Not FDA-approved for any indication
- Limited safety and efficacy data in humans
- Unknown long-term effects
- Potential for serious adverse effects
- Importance of discussing all supplements and medications with healthcare providers
- FDA has warned against its use in compounded medications
- Athletes should be warned that it is prohibited by WADA
- Many websites advertise MOTS-c “for research purposes only” but these products may be unsafe and illegal
ETHICAL AND PROFESSIONAL CONSIDERATIONS
For Pharmacists
- Be aware of FDA position on MOTS-c in compounding
- Understand legal and ethical implications of dispensing non-FDA approved peptides
- Maintain professional standards when discussing investigational compounds
- Provide evidence-based information when consulted about MOTS-c
- Consider liability issues related to non-FDA approved compounds
For Researchers
- Ensure proper informed consent in research settings
- Follow institutional and regulatory guidelines for research peptides
- Document and report adverse events
- Maintain scientific integrity in research protocols
REFERENCES
- Zheng Y, Wei Z, Wang T. MOTS-c: A promising mitochondrial-derived peptide for therapeutic exploitation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 25;14:1120533.
- USADA. What is the MOTS-c peptide? January 16, 2024. https://www.usada.org/spirit-of-sport/what-is-mots-c-peptide/
- Lee C, et al. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c promotes metabolic homeostasis and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2015 Mar 3;21(3):443-54.
- FDA. Certain Bulk Drug Substances for Use in Compounding May Present Significant Safety Risks. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/human-drug-compounding/certain-bulk-drug-substances-use-compounding-may-present-significant-safety-risks
- Lu H, et al. MOTS-c peptide regulates adipose homeostasis to prevent ovariectomy-induced metabolic dysfunction. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(4):473-485.
